The reactivity of an atom arises froma) the potential energy of the valence shellb) the existence of unpaired electrons in the valence shellc) the average distance of the outermost electron shell from the nucleusd) the sum of the potential energies of all the electron shells Click the card to flip 👆
17 Reactivity series ideas | chemistry, teaching science, science chemistry
The stability of the electrons in atoms determines not only the reactivity of an atom but its valence and the type of chemical bonds it can form. For example, carbon usually has a valence of 4 and forms 4 bonds because its ground state valence electron configuration is half-filled at 2s 2 2p 2. A simple explanation of reactivity is that it
Source Image: snexplores.org
Download Image
The reactivity of an atom is determined by the number of electrons in the valence shell, the outermost energy level of an atom.. The reactivity of an atom arises from the number of electrons in the valence shell.The valence shell is the outermost energy level of an atom, and it determines the chemical properties and reactivity of the atom.

Source Image: scitechdaily.com
Download Image
Artificial Intelligence Vibration: The Fifth Law of Physics by Alberto Roldan
The reactivity of an atom arises from a. the average distance of the outermost electron shell from the nucleus. b. the existence of unpaired electrons in the valence shell. c. the sum of the potential energies of all the electron shells. d. the potential energy of the valence shell. Verified Solution

Source Image: eslbuzz.com
Download Image
The Reactivity Of An Atom Arises From
The reactivity of an atom arises from a. the average distance of the outermost electron shell from the nucleus. b. the existence of unpaired electrons in the valence shell. c. the sum of the potential energies of all the electron shells. d. the potential energy of the valence shell. Verified Solution
The reactivity of an atom arises from ___. unpaired neutrons Ounpaired electrons number of neutrons Ounpaired protons; This problem has been solved! You’ll get a detailed solution from a subject matter expert that helps you learn core concepts. See Answer See Answer See Answer done loading.
Essential Science Terms to Unleash the Power of Science – ESLBUZZ
The physical properties of metalloids tend to be metallic, but their chemical properties tend to be non-metallic. The oxidation number of an element in this group can range from +5 to -2, depending on the group in which it is located. Table 8.4.2 8.4. 2: Elements categorized into metals, non-metals and metalloids.
The reactivity of an atom arises from a. the average distance of … | Channels for Pearson+

Source Image: pearson.com
Download Image
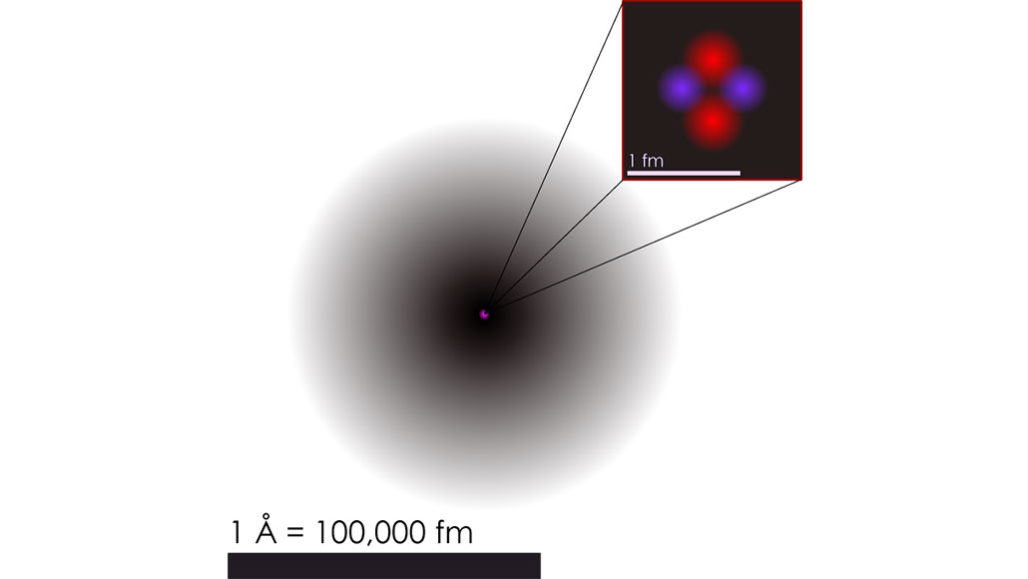
Physicists debate whether quantum math is as real as atoms | Science News
The physical properties of metalloids tend to be metallic, but their chemical properties tend to be non-metallic. The oxidation number of an element in this group can range from +5 to -2, depending on the group in which it is located. Table 8.4.2 8.4. 2: Elements categorized into metals, non-metals and metalloids.

Source Image: sciencenews.org
Download Image
17 Reactivity series ideas | chemistry, teaching science, science chemistry
The reactivity of an atom arises froma) the potential energy of the valence shellb) the existence of unpaired electrons in the valence shellc) the average distance of the outermost electron shell from the nucleusd) the sum of the potential energies of all the electron shells Click the card to flip 👆

Source Image: in.pinterest.com
Download Image
Artificial Intelligence Vibration: The Fifth Law of Physics by Alberto Roldan
The reactivity of an atom is determined by the number of electrons in the valence shell, the outermost energy level of an atom.. The reactivity of an atom arises from the number of electrons in the valence shell.The valence shell is the outermost energy level of an atom, and it determines the chemical properties and reactivity of the atom.

Source Image: linkedin.com
Download Image
How to explain to a year 9 IGCSE student what makes an atom more reactive or unreactive than others – Quora
Explanation: The second law of thermodynamics says that everything in the universe moves from order to disorder. A corollary of the second law is that everything moves to state of greater stability. Atoms will always move from an unstable structure to a more stable structure. A atom like Sodium is unstable electronically.
Source Image: quora.com
Download Image
Five Element Theory in Chinese Medicine: What the Science Says
The reactivity of an atom arises from a. the average distance of the outermost electron shell from the nucleus. b. the existence of unpaired electrons in the valence shell. c. the sum of the potential energies of all the electron shells. d. the potential energy of the valence shell. Verified Solution
Source Image: healthline.com
Download Image
Physicists are pushing the periodic table to its limits | Science News
The reactivity of an atom arises from ___. unpaired neutrons Ounpaired electrons number of neutrons Ounpaired protons; This problem has been solved! You’ll get a detailed solution from a subject matter expert that helps you learn core concepts. See Answer See Answer See Answer done loading.

Source Image: sciencenews.org
Download Image
Physicists debate whether quantum math is as real as atoms | Science News
Physicists are pushing the periodic table to its limits | Science News
The stability of the electrons in atoms determines not only the reactivity of an atom but its valence and the type of chemical bonds it can form. For example, carbon usually has a valence of 4 and forms 4 bonds because its ground state valence electron configuration is half-filled at 2s 2 2p 2. A simple explanation of reactivity is that it
Artificial Intelligence Vibration: The Fifth Law of Physics by Alberto Roldan Five Element Theory in Chinese Medicine: What the Science Says
Explanation: The second law of thermodynamics says that everything in the universe moves from order to disorder. A corollary of the second law is that everything moves to state of greater stability. Atoms will always move from an unstable structure to a more stable structure. A atom like Sodium is unstable electronically.